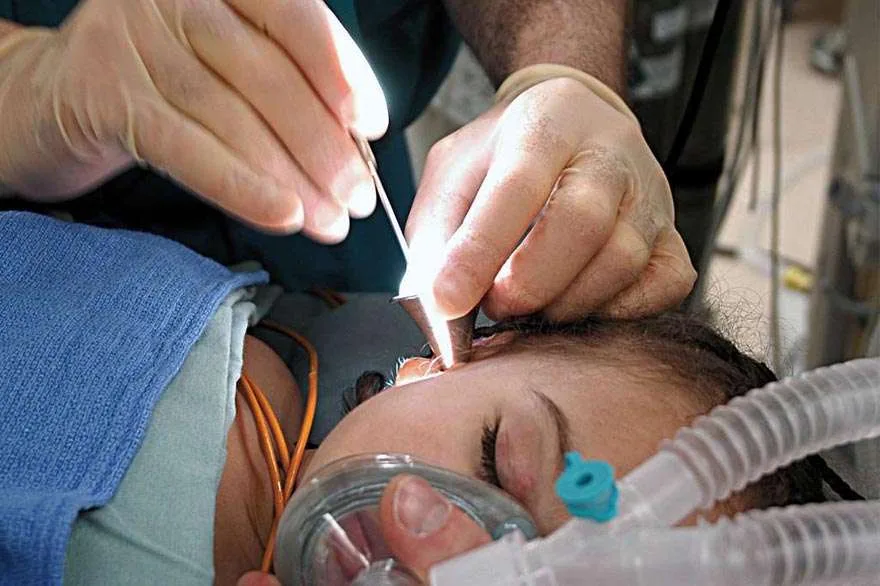
Micro Ear Surgery refers to a set of advanced surgical procedures performed on the structures of the ear using a surgical microscope and highly precise instruments. This type of surgery is commonly done to treat a variety of ear disorders, including hearing loss, chronic infections, and structural abnormalities.
Key Aspects of Micro Ear Surgery
1. Use of Microscope
- Surgeons use an operating microscope to magnify the small and delicate structures of the ear.
- Allows for better visualization and precision during the operation.
2. Common Procedures
Here are some of the most common types of micro ear surgeries:
a. Tympanoplasty
- Repair of the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
- Often done to treat perforations caused by chronic ear infections.
b. Ossiculoplasty
- Reconstruction or repair of the ossicles (tiny middle ear bones: malleus, incus, stapes).
- Helps restore hearing when these bones are damaged or malformed.
c. Stapedectomy
- Removal and replacement of the stapes bone (usually with a prosthesis).
- Commonly performed for otosclerosis, a condition that causes abnormal bone growth in the middle ear.
d. Mastoidectomy
- Removal of infected air cells in the mastoid bone, located behind the ear.
- Performed for chronic infections or cholesteatoma (an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear).
e. Cochlear Implant Surgery
- Implantation of an electronic hearing device in patients with severe hearing loss or deafness.
3. Indications
- Chronic otitis media (middle ear infections)
- Cholesteatoma
- Otosclerosis
- Tympanic membrane perforations
- Conductive hearing loss
- Congenital ear deformities
4. Benefits
- Improved hearing
- Elimination or reduction of chronic infections
- Restoration of ear anatomy
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery times compared to older techniques
5. Risks and Complications
- Hearing loss (if inner ear is damaged)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Infection
- Facial nerve damage (rare)
6. Recovery
- Typically outpatient procedures or short hospital stays
- Recovery time varies from days to a few weeks depending on the surgery
- Patients may need to avoid water exposure and heavy activity for a while

