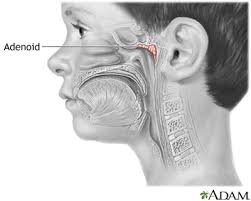
Adenoids treatment focuses on managing problems caused by enlarged or infected adenoids, especially in children. The adenoids are a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, near the roof of the throat. They help fight infections but can become chronically enlarged or inflamed, causing breathing, ear, or sinus problems.
Common Problems Caused by Enlarged Adenoids
- Nasal obstruction (mouth breathing, snoring)
- Sleep apnea (interrupted breathing during sleep)
- Recurrent ear infections
- Hearing loss due to middle ear fluid
- Chronic sinus infections
- Speech or facial development issues in children
💊 Non-Surgical Treatment
Used for mild to moderate enlargement or infection:
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays (e.g., mometasone, fluticasone)
- Help reduce inflammation
- Antibiotics
- For acute bacterial infections
- Antihistamines or decongestants
- If allergies are contributing to symptoms
- Watchful waiting
- In mild cases, especially as adenoids naturally shrink with age
🔪 Surgical Treatment: Adenoidectomy
🏥 What Is an Adenoidectomy?
- Surgical removal of the adenoids.
- Often done under general anesthesia in children.
- Frequently combined with tonsillectomy or ear tube placement (for chronic ear issues).
✅ When It’s Recommended
- Chronic nasal blockage
- Sleep-disordered breathing or apnea
- Recurrent ear infections or otitis media with effusion
- Speech or swallowing problems due to adenoid size
- Poor response to medical treatments

