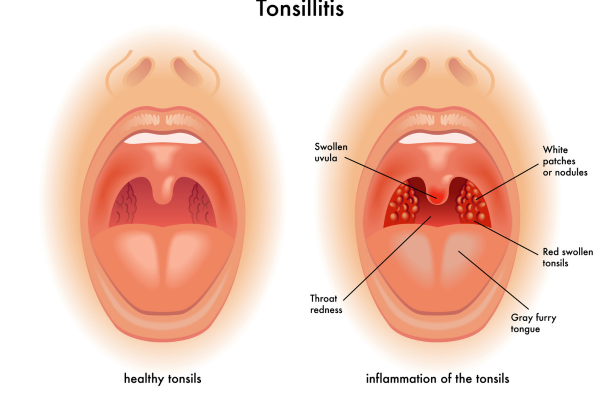
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, which are two oval-shaped lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. It is most common in children but can affect people of all ages. Tonsillitis can be viral or bacterial, and it often causes a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen tonsils.
Causes of Tonsillitis
- Viral Infections (most common):
- Adenovirus
- Rhinovirus (common cold)
- Influenza
- Epstein-Barr virus (causes mono)
- Bacterial Infections:
- Most commonly Group A Streptococcus (causes strep throat)
- Less common: other types of streptococci, staphylococcus
🧪 Symptoms
- Sore throat
- Difficulty or pain with swallowing
- Red, swollen tonsils (with or without white patches)
- Fever and chills
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Bad breath
- Hoarseness or muffled voice
- Headache or ear pain
- Fatigue or irritability (in children)
In viral cases, symptoms like runny nose or cough may also be present.
🩺 Diagnosis
- Physical exam: Looking at throat and tonsils.
- Throat swab:
- Rapid strep test: Quick, but may miss some cases.
- Throat culture: More accurate, but results take 1–2 days.
- Blood tests (in suspected mononucleosis or chronic cases).
💊 Treatment
🔹 For Viral Tonsillitis:
- Supportive care: rest, fluids, pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen), saltwater gargles.
- Antibiotics are not effective.
🔹 For Bacterial Tonsillitis:
- Antibiotics (typically penicillin or amoxicillin).
- Full course must be completed to prevent complications like rheumatic fever.
🏥 When Is Surgery Needed?
Tonsillectomy (surgical removal of the tonsils) may be considered if:
- Recurrent tonsillitis (≥7 episodes in 1 year, or ≥5/year for 2 years)
- Chronic tonsillitis unresponsive to treatment
- Obstructive sleep apnea due to enlarged tonsils
- Peritonsillar abscess (repeated or severe)
⚠️ Possible Complications (if untreated or severe)
- Peritonsillar abscess (collection of pus)
- Airway obstruction
- Ear infections
- Spread of infection (e.g., to the neck or bloodstream)
- Rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation (post-strep)
🛡️ Prevention Tips
- Good hand hygiene
- Avoid close contact with infected people
- Don’t share utensils or drinks
- Replace toothbrush after infection clears

